|
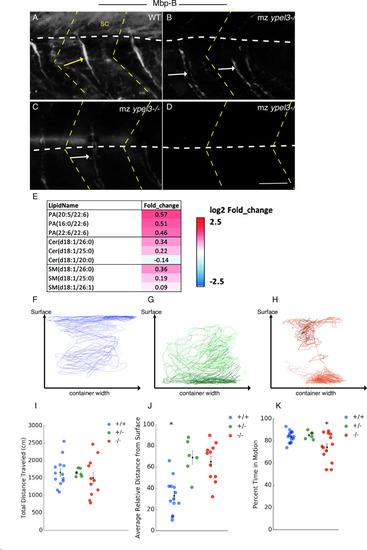
Ypel3 is required for myelination and locomotory behavior.(A-D) Myelin basic protein b (Mbpb) expression. Lateral views of embryos labeled for Mbpb at 7 dpf. (A) WT. (B-D) mz ypel3 mutants. Mbpb levels are undetectable in the spinal cord (sc) and variably reduced in the motor nerves (arrows). Yellow arrow shows a fasciculated nerve with a homogenous distribution of the Mbpb signal in WT. White arrows show defasciculated nerves in mz ypel3 mutants. Mutant nerves have variable levels and an uneven distribution of Mbpb. White horizontal dashed lines indicate the spinal cord ventral border in (A-B) and the horizontal myoseptum in (C-D). Yellow dashed chevron: somite borders. Scale bar: 25 μm. (E) Lipidomics panel showing an increase in phosphatic acids (PA) and ceramides (Cer) except Cer(d18:1/20:0) in the mz ypel3 mutant compared to WT. (F-K) Adult mz ypel3-/- mutants have behavioral and locomotion defects. (F-H) Representative swimming traces of WT (F), heterozygous ypel3b1309 (G), and homozygous mz ypel3b1309 mutants (H). (I-K) Quantification of total distance traveled (I), average relative distance from the surface (J), and percent time spent in motion (K). +/+: WT. +/-: heterozygous. -/-: mz ypel3 mutants. Bars represent +/- standard error of the mean (+/- SEM).
|