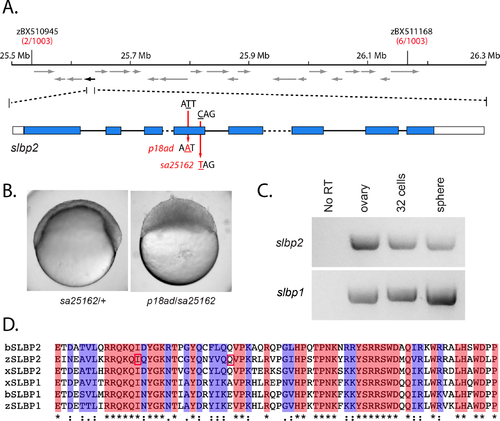
screeching halt encodes SLBP2. A. The srh mutation maps to a 600 kb interval on chromosome 21 flanked by zBX510945 and zBX511168. Recombinants identified between the mutation and the marker per total meiotic events examined is noted below each marker in red. The interval contains 21 predicted ORFs (arrows). The black arrow (on the reverse strand) corresponds to slbp2. The predicted exon-intron structure is indicated below. Note: intron 3 (568 bp) and intron 5 (1961bp) are not drawn to scale (dashed lines) due to size. Mutations corresponding to srhp18ad (T to A, Iln to Asn) and srhsa12562 (C to T, Glu to stop) map to exon 4. B. The sa25162 allele fails to complement srhp18ad. Embryos from sa25162/+ females and ten p18ad/sa25162 trans-heterozygous females, with at least 50 embryos per female (n = 880), shown at 6 hpf. C. RT-PCR of slbp2 (top) and slbp1 (bottom) from wild-type cDNA (ovary, 32-cell and sphere stage). D. SLBP RBDs from zebrafish (zSLBP1 and zSLBP2), Xenopus (xSLBP1 and xSLBP2) and Bovine (bSLBP1 and bSLBP2) were aligned using Clustal Omega [53]. The Iln residue that is mutated to Asn in srhp18ad and the Glu residue that is mutated to a stop codon in slbp2sa12562 are boxed in red. The ?*? indicates identical residues, ?:? or ?.? indicate similar residues. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008652.g008
|
