Fig. S12
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190826-4
- Publication
- Whitesell et al., 2019 - foxc1 is required for embryonic head vascular smooth muscle differentiation in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
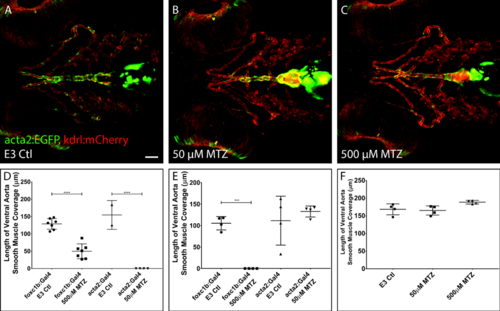
Treatment of Metronidazole (MTZ) does not affect vessel patterning or vSMC coverage along the ventral aorta in embryos. A-C) 4 dpf acta2:EGFP, kdrl:mCherry E3 control embryos lacking the NTR construct (A) show that treatment with MTZ does not affect vascular patterning or development of vSMC when using the same doses for acta2:Gal4 (B) or foxc1b:Gal4 (C) ablation. n = 4 embryos per panel. D) Quantification of vSMC coverage from data in Figure 9 A-D, using live transgenics (foxc1b:Gal4; UAS-NTR:mCherry or acta2:Gal4; UAS-NTR:mCherry) at 4 dpf. E) Quantification of vSMC coverage in Figure 9 E-H, using acta2 mRNA in situ hybridization. F) Quantification of vSMC coverage using live transgenics lacking NTR construct (acta2:EGFP, kdrl:mCherry). Data points in D-F represent individual embryos. *** = p < 0.001, ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Scale bar represents 50 µm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 453(1), Whitesell, T.R., Chrystal, P.W., Ryu, J.R., Munsie, N., Grosse, A., French, C.R., Workentine, M.L., Li, R., Zhu, L.J., Waskiewicz, A., Lehmann, O.J., Lawson, N.D., Childs, S.J., foxc1 is required for embryonic head vascular smooth muscle differentiation in zebrafish, 34-47, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.