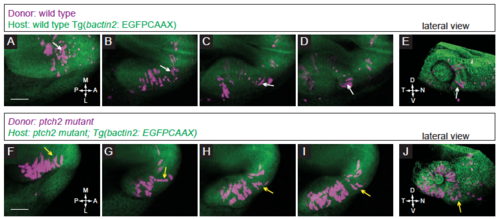
Fig. S3
|
Localization and movement of transplanted cells in control conditions. (A-E) Transplantation of wild type donor cells into a wild type host. (A-D) Donor cells move out of the midline region, through the prospective optic stalk, and into the optic cup. Note the bipolar, elongated morphology of the cell contributing to the nasal optic fissure (white arrows). (E) Lateral view of 3D rendering of final timepoint. (F-J) Transplantation of ptch2tc294z mutant donor cells into a ptch2tc294z mutant host. (F-I) Many donor cells in this movie start already within the optic vesicle. Following cells that emerge from the midline region, some cells exhibit and maintain this morphology through the optic stalk and into the optic cup. Other cells (yellow arrows) lose their bipolar morphology and contribute to the optic stalk. (J) Lateral view of 3D rendering of final timepoint. Scale bar, 50 ?m. |