Fig. 7-S8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180801-31
- Publication
- LLeras Forero et al., 2018 - Segmentation of the zebrafish axial skeleton relies on notochord sheath cells and not on the segmentation clock
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
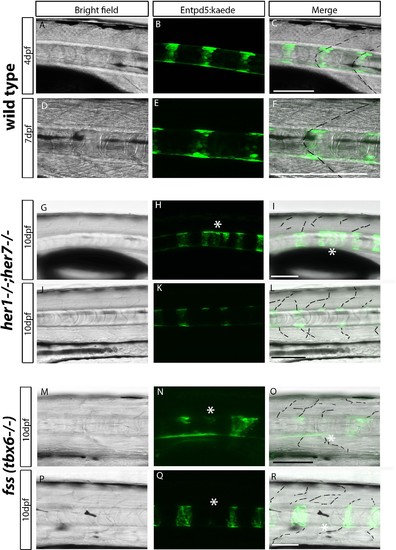
Chordacentra always align with the myotome boundaries in wild type larvae, but not in mutants. (A-R) Live confocal images of entpd5:Kaede in the trunk of wild type, her1?/?;her7?/? and fss (tbx6?/?) larvae, in lateral view, anterior to the left. (A-F) Live images at 4 dpf and 7 dpf show entpd5:kaede positive notochord segments (B and E) are aligned with the myotome boundary (A and D) in wild types. In her1;her7 (G-L) and tbx6 (M-R) mutants at 10 dpf, the myotome boundaries are disrupted and are no longer in strict alignment with the entpd5:kaede segment. Asterisks (*) denote defects in axial segmentation; dashed lines trace myotome boudaries and boudary fragments. Scale bars are 100 Ám. |