Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180703-50
- Publication
- Sorrells et al., 2018 - Spliceosomal components protect embryonic neurons from R-loop-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
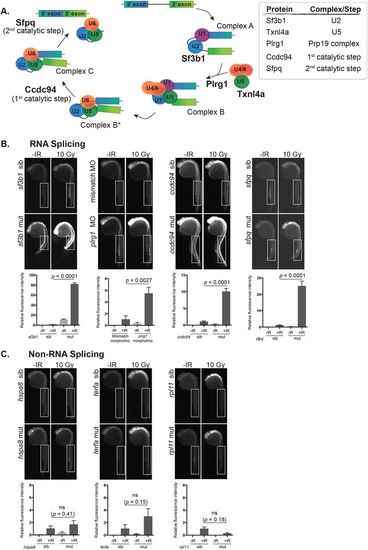
Disruption of RNA splicing factor genes sensitizes embryonic neurons to IR-induced apoptosis. (A) Schematic of the RNA splicing pathway showing the steps in which the RNA splicing factors used in this study are expected to function. (B) Splicing factor mutant and sibling embryos, or morphants and controls, were exposed (+IR) or left unexposed (-IR) to 10 Gy IR and analyzed 3 h later for active caspase-3. All embryos were irradiated at 24 hpf, except sf3b1hi3394aTg mutants and siblings which were irradiated at 22 hpf before the neurodegenerative phenotype became severe. Upper panels show representative images of active caspase-3 staining in each genotype or treatment group. Lower panels show the quantification of active caspase-3 staining for each genotype measured in the spinal cord area within the boxed regions. At least 10 embryos were quantified per genotype and treatment condition and fluorescence intensity from sibling +IR was normalized to one to account for non-specific background staining. (C) Non-splicing factor mutants and siblings were analyzed as in B. ns, not significant; error bars represent s.e.m. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |