Fig. 4
|
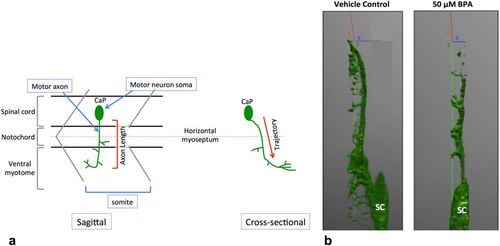
Motor neuron trajectory from a sagittal and cross sectional view. At 18 hpf, primary motor neurons start to exit the ventral root of the spinal cord. By 48 hpf each somite has one set of caudal (CaP), middle (MiP) and rostral (RoP) primary motor neurons innervating each side of the spinal segment67. For simplicity, here we only show the CaP motor neuron. (a) CaP motor axons project ventrally from the SC to the ventral myotome. Axon length is conventionally measured from the sagittal plane, with the assumption that motor axons in control embryos and embryos with motor axon abnormalities follow the same trajectory. (b) Defective motor axons have a normal trajectory from the spinal cord. Tg:mnx1-GFP embryos exposed to BPA have a similar motor axonal trajectory through the Z axis (green) as vehicle controls (N?=?3 biological replicates). |