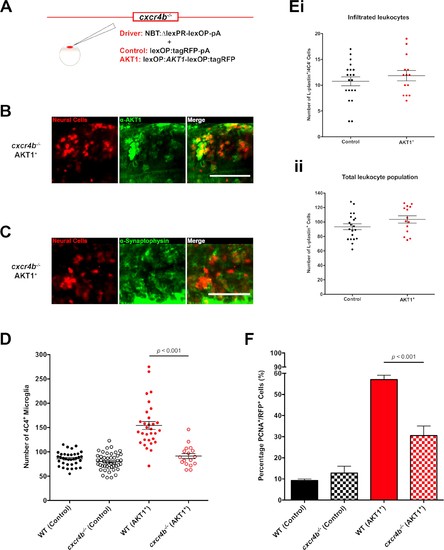
Fig. 5
|
Cxcr4b signaling is required for the increase in microglia numbers following AKT1 overexpression. (A) To achieve expression in neural cells in the cxcr4b-/- mutant zebrafish line, a driver plasmid containing the NBT promoter (NBT:?lexPR-lexOP-pA) was co-injected together with either a lexOP:AKT1-lexOP:tagRFP plasmid to induce AKT1 expression or together with a lexOP:tagRFP-pA plasmid to achieve control RFP expression. Immunohistochemistry expression of (B) the human AKT1 protein and (C) Synaptophysin in the AKT1-expressing cells in the cxcr4b-/- mutant fish at 8 dpf. (D) Quantification of the number of microglia in wild-type (WT)(cxcr4b+/+) controls, cxcr4b-/- controls, and following AKT1 overexpression in WT larvae and cxcr4b-/- fish at 8 dpf (WT AKT1: 154.2 ▒ 8.15, n = 31 larvae; cxcr4b-/- AKT1: 91.4 ▒ 5.22, n = 17 larvae, p<0.001, N = 3). (Ei) Quantification of the number of infiltrated leukocytes (L-plastin+/4C4-) into the brain parenchyma in control and AKT1-positive cxcr4b-/- fish at 8 dpf (cxcr4b-/- Control: 10.8 ▒ 0.85, n = 20 larvae; cxcr4b-/- AKT1: 11.9 ▒ 1.00, n = 14 larvae, p=0.408 (n.s.), N = 3). (Eii) Quantification of the total L-plastin+ leukocyte population in control cxcr4b-/- larvae and following AKT1 overexpression at 8 dpf (cxcr4b-/- Control: 93.4 ▒ 4.05, n = 20 larvae; cxcr4b-/- AKT1: 103.5 ▒ 5.00, n = 14 larvae, p=0.122 (n.s.), N = 3). (F) Quantification of the level of proliferation rates in control-RFP and AKT1-expressing cells in WT and cxcr4b-/- fish at 8 dpf (WT AKT1: 57.1 ▒ 2.03%, n = 17 larvae, cxcr4b-/- AKT1: 30.5 ▒ 4.53%, n = 5 larvae, p<0.001, N = 2). Error bars represent mean ▒SEM. Images were captured using a Zeiss LSM710 confocal microscope with a 20X/NA 0.8 objective. Scale bars represent 100 Ám. |