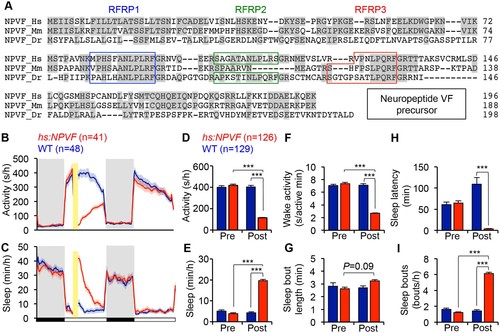
NPVF overexpression decreases locomotor activity and increases sleep. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of human (Hs), mouse (Mm), and zebrafish (Dr) NPVF preproproteins. Colored boxes demarcate identified or predicted mature peptide sequences. Note that the mouse NPVF protein lacks RFRP2. (B?I) NPVF overexpression decreased locomotor activity (B,D) and increased sleep (C,E) in transgenic animals compared to WT siblings and to pre-HS. Yellow bar indicates heat shock. Pre- and Post-HS data is calculated for the day of HS. White and black bars under behavioral traces indicate day (14 h) and night (10 h), respectively. NPVF overexpression decreased wake activity (F), decreased sleep latency (time to first sleep bout following lights on in the morning Pre-HS, or following HS in post-HS measurement) (H) and increased sleep bout number (I), and also caused a trend of increased sleep bout length (G). Mean ± SEM from one representative experiment (B,C), or three pooled experiments (D?I) are shown. n = number of animals. ***p<0.0001 by Two-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak test.
|

