Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180411-10
- Publication
- Veil et al., 2017 - Maternal Nanog is critical for the zebrafish embryo architecture and for cell viability during gastrulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
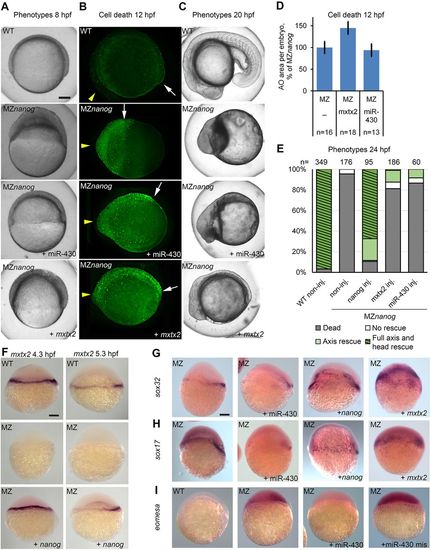
mxtx2 or miR-430 injection at the 1-cell stage rescues epiboly but not cell death in MZnanog embryos. (A-C) MZnanog embryos were injected at the 1-cell stage with mxtx2 mRNA or miR-430, as indicated, or not injected. Wild-type (WT) embryos were used as stage control. (A) Representative phenotypes at 8?hpf. Note the thinning of blastoderm and epiboly progression in injected MZnanog embryos compared with non-injected MZnanog. (B) Staining for dead cells in 12?hpf embryos. Yellow arrowheads and white arrows point to anterior and posterior ends of embryo axes, respectively. (C) Representative phenotypes at 20?hpf. (D) Dead cells rescue statistics: neither mxtx2 nor miR-430 mRNA injection reduced cell death in MZnanog; n, number of scored embryos. Error bars represent s.e.m. (E) Phenotype rescue statistics after 24?hpf. One-cell stage MZnanog embryos were injected as indicated or left non-injected; classes used for scoring are shown in Fig. 5M-O. Numbers of embryos are indicated above the bars. (F-I) In situ hybridization for mxtx2 at 4.3 and 5.3?hpf (F), sox32 at 8?hpf (G), sox17 at 8?hpf (H) and eomesa at 6?hpf (I). Genotypes are indicated top left as MZ (MZnanog) or WT, injected substances are indicated bottom right. Lateral views. Scale bars: 100?Ám. |