Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170815-37
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2017 - microRNA-206 modulates an Rtn4a/Cxcr4a/Thbs3a axis in newly forming somites to maintain and stabilize the somite boundary formation of zebrafish embryos.
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
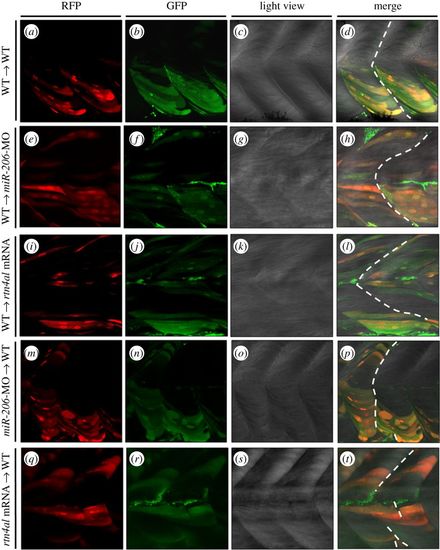
Transplantation of cells derived from either miR-206-MO- or rtn4al-mRNA-injected embryos causes recipient embryos to generate somite boundary defects. (a?d) After Dextran was injected into Tg(?-actin:RFP) embryos at the one-cell stage, cells were taken from donor embryos at 4 hpf and transplanted into WT embryos at 4.7 hpf. Embryonic somite boundary development was observed when embryos were 48 hpf. (a) Differentiated muscle cells among the transplanted cells were marked by RFP. (b) All transplanted cells were marked with green fluorescent signal. (c) Somite morphology was observed under microscopic light field. (d) Somite boundary was normally formed. (e?h) Transplanted cells from Dextran-injected Tg(?-actin:RFP) embryos to miR-206-MO-injected embryos. (i?l) Transplanted cells from Dextran-injected Tg(?-actin:RFP) embryos to rtn4al-mRNA-injected embryos. (m?p) Transplanted cells from Dextran- and miR-206-MO-injected Tg(?-actin:RFP) embryos to WT embryos. (q?t) Transplanted cells from Dextran- and rtn4al-mRNA-injected Tg(?-actin:RFP) embryos to WT embryos. Broken line indicates formation of the somite boundary. |