Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160707-40
- Publication
- Lisse et al., 2016 - Paclitaxel-induced epithelial damage and ectopic MMP-13 expression promotes neurotoxicity in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
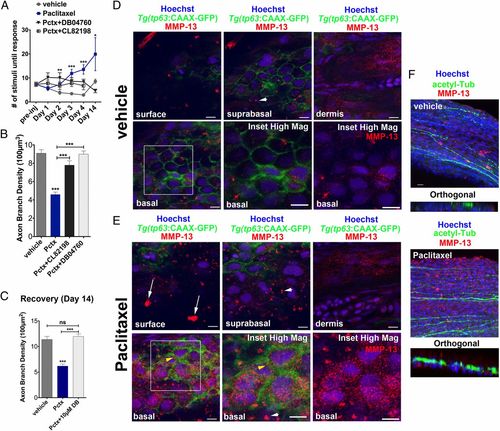
MMP-13 inhibition improves adult paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity. (A) Improved touch response upon coadministration of paclitaxel and either DB04760 or CL-82198 following four injections (n = 7, 7-12 fish per group) and complete rescue by day 14 in DB04760 coadministered animals (n = 2, 5 fish). (B and C) Axon branch density in distal caudal fin is rescued upon coadministration of paclitaxel and either DB04760 or CL-82198 when assessed 1 d (B) (n = 3, 7-12 fish per group) or 10 d (C) (n = 2, 5 fish per group) after the last injection. (D and E) MMP-13 immunofluorescence staining (red) 1 d after the last injection shows MMP-13 up-regulation specifically in basal keratinocytes (yellow arrowheads) of Tg(tp63:CAAX-GFP) fish injected with paclitaxel (E) and low MMP-13 expression in vehicle controls (D). Imaging was performed using identical settings. Dermal cells in both vehicle and paclitaxel-injected fish have similar MMP-13 expression levels. White arrowheads depict large distinctive MMP-13 clusters. (E) White arrows depict clusters of MMP-13-positive cellular debris at the skin surface, indicative of increased cell shedding. (Scale bar, 5 µm.) (F) MMP-13 staining (red) is adjacent to, but not within, DRG axons (green). (Scale bar, 10 µm.) *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. ac-tub, acetylated tubulin; Pctx, paclitaxel. |