Fig. 5 S3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160321-27
- Publication
- Eom et al., 2015 - Long-distance communication by specialized cellular projections during pigment pattern development and evolution
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
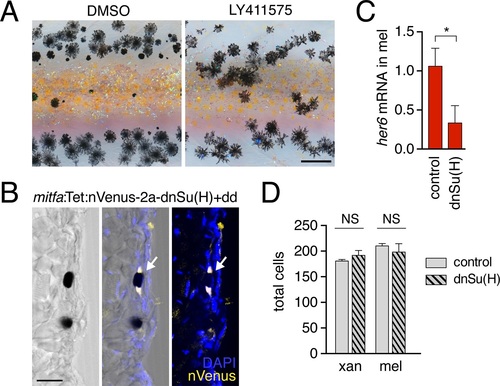
Notch signaling inhibition.(A) Treatment with Notch inhibitor LY411575 during adult pigment pattern development caused defects in melanophore clearance and stripe consolidation. (B) Induction of mitfa:Tet:nVenus-2a-dnSu(H) in melanophores of stable transgenics reduced expression of Notch target gene her6 (p<0.05) in isolated melanophores, relative to non-transgenic but dd-treated controls. (C) Melanophore of fish mosaically expressing mitfa:Tet:nVenus-2a-dnSu(H) stained for nuclear-localizing Venus by immunohistochemistry (arrow); nucleus is bipartite. Scale bar. (A) Extended induction of mitfa:Tet:nVenus-2a-dnSu(H) in melanophores did not affect total numbers of xanthophores (t8=0.92, p=0.4) or melanophores (t8=0.70, p=0.5) relative to dd-treated non-transgenic controls. Fish analyzed here were performed concurrently with those of Figure 4 - figure supplement 2E and employed the same controls. Scale bars: 200 Ám (A); 20 Ám (C). |