Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150504-49
- Publication
- Yu et al., 2015 - Hedgehog signaling regulates dental papilla formation and tooth size during zebrafish odontogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
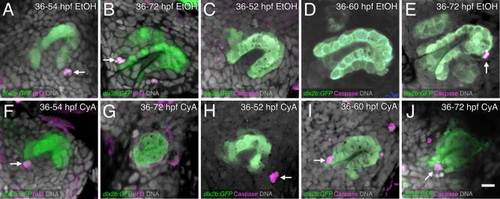
Hedgehog inhibition induces unusual late tooth germ apoptosis but proliferation appears relatively normal. A?J: Antibody labels (magenta) for pH3 (proliferation; A,B,F,G) or Caspase 3 (apoptosis; C?E,H?J) in the dlx2b:GFP reporter line (green) with DNA label (gray). Treatments are EtOH control (A?E) or with CyA exposure starting at 36 hpf (F?J). pH3 proliferation staining at or near the base of the dental epithelium in control (A) and CyA treated (F) tooth germs at 54 hpf (arrows). Proliferation is visible in a 72 hpf control tooth germ (arrow, B), but only background staining is seen after CyA treatment (G). C?E: Caspase 3 apoptosis staining is absent from control tooth germs, except near the tip of tooth #1 at 72 hpf (arrow, D). Apoptosis can be seen in the tooth forming region after 36?52 hpf CyA exposure but not localized to the tooth germ (arrow, H). Caspase 3-positive cells in the dental epithelium after 36?60 hpf CyA treatment (arrow, I). An apoptotic cell is visible in the base of the tooth germ after 36?72 hpf CyA exposure (arrow, J). Tooth germ orientations are as in Figure 1. Scale bar = 10 Ám in J. |