Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150422-55
- Publication
- George et al., 2015 - An early requirement for nkx2.5 Ensures first and Second heart field ventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
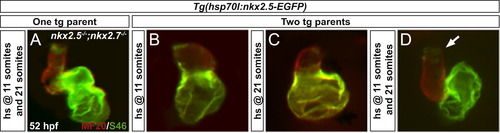
Rescue of nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7-/- embryos validates a dose-dependent role of nkx2.5 and suggests a unique function for nkx2.7. Frontal views, anterior to the top, of MF20/S46 immunofluorescence (as in Fig. 3) at 52 hpf. In contrast to nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7-/- offspring of a single Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP) carrier following heat shock at one time point (Fig. 5L-O), a transgenic nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7-/-embryo subject to heat at 11 somites and 21 somites demonstrates enhanced rescue of ventricular and atrial size and identity defects (A). Despite only moderate improvement in offspring from a cross of two transgenic parents at 11 somites (B) and 21 somites (C), performing heat shock at two time points to augment Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP) expression further yields normalization of cardiac chamber morphology (D). Yet, residual, ectopic S46+ cardiomyocytes highlight chamber identity abnormalities in the late-differentiating SHF-derived population (D; arrow). |
| Antibodies: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 400(1), George, V., Colombo, S., Targoff, K.L., An early requirement for nkx2.5 Ensures first and Second heart field ventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood, 10-22, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.