Fig. S11
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150416-20
- Publication
- Cheng et al., 2015 - Nephron proximal tubule patterning and corpuscles of Stannius formation are regulated by the sim1a transcription factor and retinoic acid in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
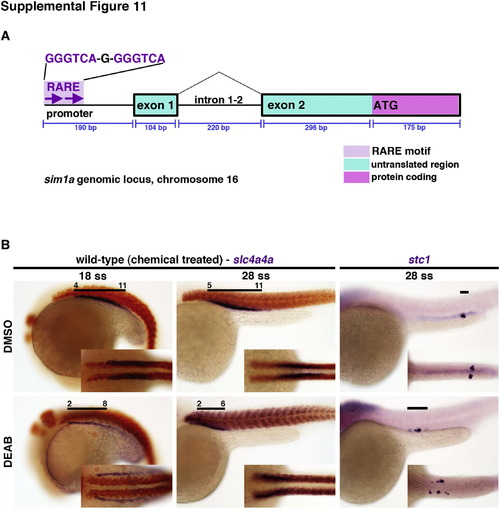
The inhibition of RA biosynthesis through DEAB exposure in wild-type embryos leads to abnormal nephron segmentation. (A) Diagram of the genomic sim1a locus, with the sim1a coding region and 52 upstream sequence including a putative RARE element. (B) Wild-type embryos were treated from 75% epi to 5–7 ss with DMSO vehicle alone as the control or 1.67×105 M DEAB. WISH analyses were performed to label pan-proximal (nbc1) or CS (stc1) kidney domains (purple), and somite labeling by smyhc1 expression (red), at different time points. Black lines indicate segment domains with respect to somite numbers. Embryo anterior is to the left. Abbreviations: CS – corpuscles of Stannius; DEAB – 4-diethylaminobenzaldehyde; epi – epiboly; RA – retinoic acid; RARE – retinoic acid response element; ss – somite stage; WISH – whole mount in situ hybridization. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 399(1), Cheng, C.N., Wingert, R.A., Nephron proximal tubule patterning and corpuscles of Stannius formation are regulated by the sim1a transcription factor and retinoic acid in zebrafish, 100-16, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.