Fig. 2
|
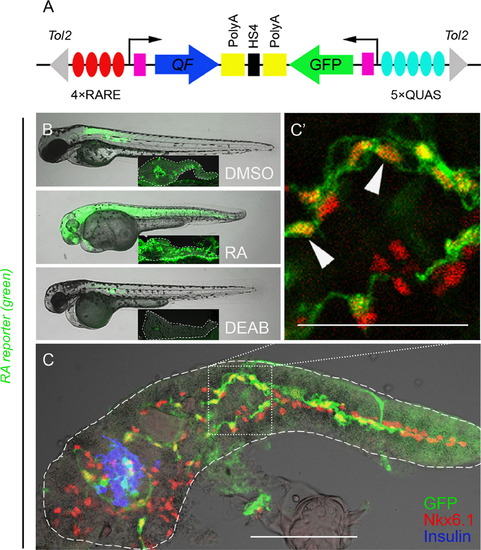
PNCs are RA-responsive. (A) Schematic of the RA reporter, 4xRARE-cFos:QF; QUAS:GFP. Expression of transcription factor QF (blue arrow) is driven by 4 RA-responsive elements (4xRARE, 4 red ovals). In the opposite orientation, GFP coding sequence (green arrow) is cloned downstream of 5 QF upstream activating sites (5xQUAS, 5 cyan ovals). QF binds to QUAS sequence to activate GFP expression. HS4 Insulator sequence (black rectangle) prevents the interference between the two transcriptional units. Pink rectangles represent cfos minimal promoters. The transgene is flanked by Tol2 arms (gray triangles). (B and C) Fluorescence images of RA reporter larvae. The channel of green fluorescence shows the RA reporter signal. (B) Compared to DMSO control, 3 dpf larvae treated with exogenous RA or DEAB increase or decrease their RA reporter signal, respectively. The larvae were incubated from 1?3 dpf with either 10 μM RA, 25 μM DEAB or DMSO. Insets show images of dissected pancreata from treated larvae at 5 dpf, outlined in white dashed lines. (C) RA-responsive cells are Nkx6.1+ in the larval pancreas. A single-plane confocal image of a larval pancreas dissected at 5 dpf and immunostained for Nkx6.1 and Insulin. Arrowheads indicate examples of GFP+ Nkx6.1+ cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Conditions: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Protruding-mouth to Day 5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 394(1), Huang, W., Wang, G., Delaspre, F., Vitery, M.D., Beer, R.L., Parsons, M.J., Retinoic acid plays an evolutionarily conserved and biphasic role in pancreas development, 83-93, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.