Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140421-13
- Publication
- Zigman et al., 2014 - Hoxb1b controls oriented cell division, cell shape and microtubule dynamics in neural tube morphogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
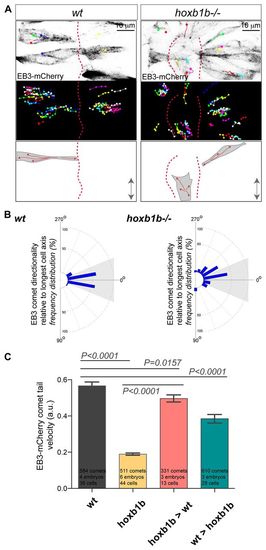
Hoxb1b is essential for plus end microtubule dynamics. (A) Live imaging of neuroepithelial cells of EB3-mCherry mRNA-injected wild type and hoxb1b-/- at r3/r4 with single EB3-mCherry comets marked as colored dots (presenting last position) connected with lines (movement over time) between 15 and 17 hpf. Top panels show a single time point, middle panels show tracks of individual EB3-mCherry comets projected over time revealing the effect on Hoxb1b loss on the comet directionality. MT plus-end dynamics are schematized at the bottom. Double arrows indicate the embryo anterior-posterior axis. Red dashed lines indicate midline. (B) Quantitation of single EB3-mCherry comets when tracked over time in respect to the A/P axis (0°) demonstrating quantitative defects in MT growth in hoxb1b-/- (n=6 embryos) compared with wild-type controls (n=4 embryos). (C) Decreased velocity of individual EB3-mCherry comets in hoxb1b-/- compared with wild type. Note rescue of EB3-mCherry comet dynamics in hoxb1b-/- cells when transplanted into wild-type hosts and partial (but significant) decrease in comet velocity in wild-type cells when transplanted into hoxb1b-/- embryos. Results presented as mean ± s.e.m. The data used for quantification of wild type and hoxb1b-/- in B and C originate from the same data set. |