Fig. S4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140416-30
- Publication
- Elks et al., 2013 - Hypoxia inducible factor signaling modulates susceptibility to mycobacterial infection via a nitric oxide dependent mechanism
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
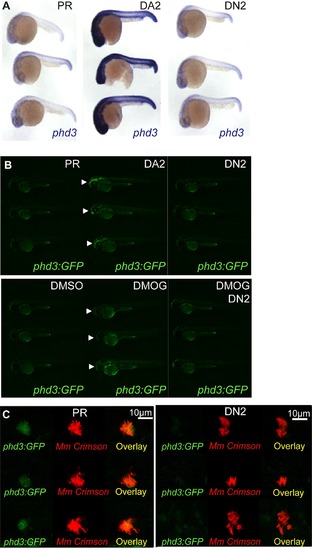
Dominant hif-2αa variants exhibit the same effects on phd3 expression as the equivalent dominant hif-1αb variants. (A) Photomicrographs of 24 hpf embryos after injection with dominant active (DA2) and dominant negative (DN2) hif-2αa constructs or phenol red (PR) as a control, showing expression of the Hif-α target gene phd3 by in situ hybridization. (B) Fluorescent photomicrographs of 48 hpf phd3:GFP embryos injected with dominant active with dominant active (DA2) and dominant negative (DN2) hif-2αa constructs or phenol red (PR) as a control. Upper panels show that DA2 increases the expression of phd3:GFP compared to PR and DN2 (white arrows). Lower panels show that DN2 can block the increased expression of phd3:GFP in the yolk (white arrows) after DMOG treatment. (C) phd3:GFP embryos were injected at the 1 cell stage with dominant negative hif-2αa RNA (DN2) or phenol red (PR) as a negative control. 60 embryos of each were screened for phd3:GFP expression using confocal microscopy and the 3 brightest areas of phd3:GFP expression were imaged and showed co-localization Mm infection. In the DN2 group GFP laser levels and confocal settings were increased until background green fluorescence was visible showing no specific co-localisation with Mm. |