Fig. 5
|
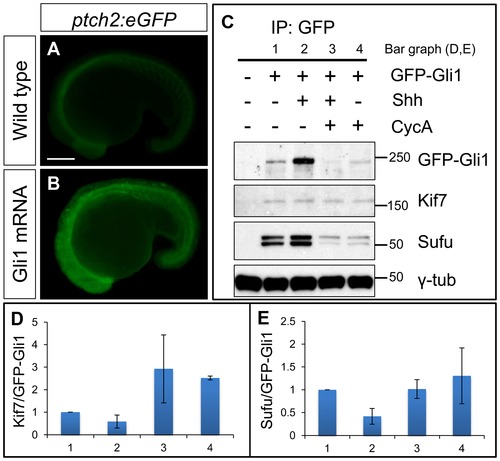
Functional tagged Gli1 associates with Kif7 and Sufu in a Hh dependent manner. (A,B) Lateral views of 20ss ptc2:eGFP embryos uninjected (A) and injected with mCherry-Gli1 mRNA (B) showing the ectopic activation of ptch2:eGFP reporter. Scale bar: 150 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of anti-GFP immune-precipitates from uninjected embryos or embryos injected with a combination of GFP-Gli1 and/or Shh mRNA and/or exposed to cyclopamine (CycA); note the stabilization of GFP-Gli1 in the presence of ectopic Shh and a reduced association between Kif7 and Gli1 (see D for quantification); inhibition of Hh pathway activity by cyclopamine reverses this effect and further enhances the association. The inhibitory association of Sufu and Gli1 is also reduced in response to pathway activation by Shh mRNA injection (see E for quantification). (D) The ratio of Kif7:GFP-Gli1 from experiments described in panel (C); WT (1), Shh mRNA injected (2), CycA exposed and Shh mRNA injected (3), and CycA exposed embryos; showing reduced Kif7-Gli1 association upon pathway activation and increased association when the pathway is inhibited. Error bars represent standard deviation obtained from three independent biological replicates. (E) The ratio of Sufu:GFP-Gli1 from experiments described in panel (C); WT (1), Shh mRNA injected (2), CycA exposed and Shh mRNA injected (3), and CycA exposed embryos; showing reduced Sufu-Gli1 association upon pathway activation and restoration of this association upon pathway inhibition. Error bars represent standard deviation obtained from three independent biological replicates. |