Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140311-19
- Publication
- McCarroll et al., 2013 - Fgf3 and Fgf10a work in concert to promote maturation of the epibranchial placodes in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
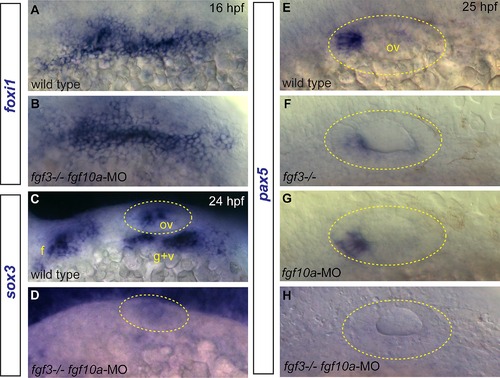
Effects of Fgf3+10a loss on development of EB and otic placodes. (A, B) foxi1 expression detected by in situ hybridization in 16 hpf zebrafish embryos reveals no difference in distribution of EB placode precursors in control (A) and fgf3-/-;fgf10a-MO (B) conditions. (C, D) sox3 expression detected by in situ hybridization in 24 hpf zebrafish embryos. Control shows expression of sox3 transcripts in the otic vesicle (outlined in yellow), and the EB placodes (C); sox3 expression is lost in these structures in the fgf3-/-;fgf10a-MO embryo (D). (E-H) pax5 expression detected by in situ hybridization in 25 hpf embryos. Control conditions show expression of pax5 in the anterior portion of the otic vesicle (E). Whereas only partial loss of pax5 was observed in fgf3-/- (F) or fgf10a-MO (G) embryos, complete loss of pax5 expression was observed in fgf3-/-;fgf10a-MO embryo (H). Abbreviations: f, facial placode; g+v glossopharyngeal/vagal placode; ov, otic vesicle. |