Fig. 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140226-28
- Publication
- Alexandre et al., 1996 - Ectopic expression of Hoxa-1 in the zebrafish alters the fate of the mandibular arch neural crest and phenocopies a retinoic acid-induced phenotype
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
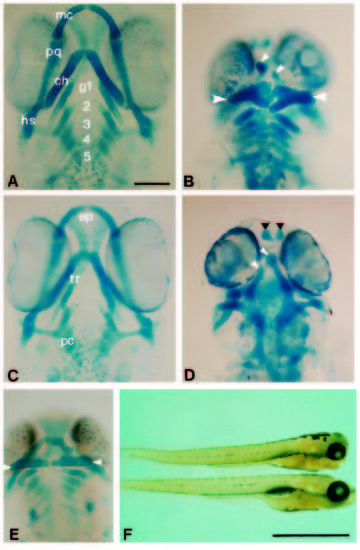
Hoxa-1 overexpression causes abnormal development of the head skeleton as shown in ventral views of alcian blue-stained larvae. (A) Control larva. The Meckel’s (mc) and palatoquadrate (pq) cartiliages are formed from the first pharyngeal arch mesenchyme. The ceratohyals (ch) and hyosymplectics (hs) are formed from the second arch mesenchyme. The gill arches (g) are shown by numbers. (B) A larva which was injected with Hoxa-1 RNA showing abnormal development of the jaws. The first arch derivatives are absent and a broadened pair of ceratohyals are formed (large arrowheads). Small arrowheads indicate the tip of the abnormally formed trabeculae. (C) Control larva showing the ventral neurocranium. The anterior ethmoid plate (ep), trabeculae (tr) and posterior parachordals (pc) are evident. (D) Dorsal view of the same embryo as in (B). The trabeculae are malformed (white arrowheads), the ethmoid cartilages exist as separate pieces anteriorly (black arrowheads) and the parachordals are normal. (E) A larva that was treated with RA at the onset of gastrulation showing the abnormally formed jaws. The forked ceratohyals are arrowed. (F) Two larvae showing the formation of the jaws at 4 days. The top one has been injected with Hoxa-1 and lacks the protruding jaws evident in the control larva below. Scale bar, 100 μm (A-E) or 1 mm (F). |