Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131108-24
- Publication
- Gratacap et al., 2013 - Mucosal candidiasis elicits NF-κB activation, proinflammatory gene expression and localized neutrophilia in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
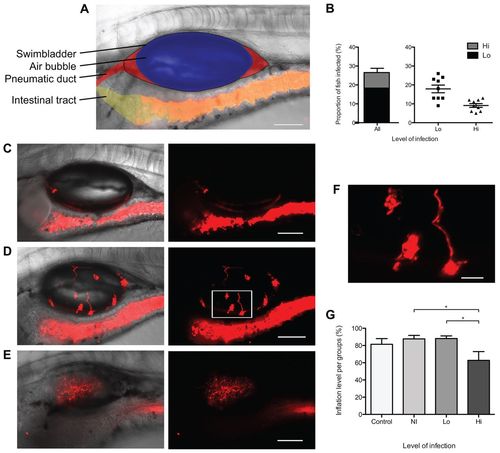
Candida albicans infects the swimbladder of juvenile zebrafish. (A?F) Cohorts of 20 AB fish were infected by immersion with C. albicans CAF2-dTomato and imaged by confocal microscopy at 5 dpi (8 dpf). (A) C. albicans immersion, non-infected (NI) with pseudo-coloring; black outline of the swimbladder; blue: swimbladder air bubble; red: fluid filled regions, anterior with pneumatic duct and posterior; yellow: intestinal tract with red-fluorescent C. albicans. (B) Level of infection at 5 dpi, low-level infection (Lo; 1 to 20 yeasts), high-level infection (Hi; over 20 yeast cells) and combination of both. Left is a stacked chart depicting the overall percentage of infected fish, divided by intensity of infection. Right shows the mean and standard errors for nine independent experiments. (C?F) Representative images of different levels of infection after C. albicans immersion: (C) low-level infection; (D,E) high-level infection, with (D) inflated and (E) non-inflated swimbladder. Animated z-stack of panel D is shown in supplementary material Movie 1. (F) Magnification of panel D (white box). Scale bars: 100 μm (A,C?E) and 20 μm (F); maximum projection slices n=16 for all images. (G) Level of inflation of the swimbladder in different groups. Average and standard error of ten independent experiments are shown. One-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test; *P<0.05. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. |