Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131031-15
- Publication
- Jao et al., 2013 - Efficient multiplex biallelic zebrafish genome editing using a CRISPR nuclease system
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
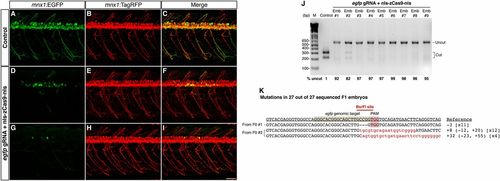
Efficient disruption of the Tg(-5.1mnx1:EGFP) transgene by Cas9 results in mosaic EGFP expression in the motoneurons. egfp gRNA (6 or 30 pg) and nls-zCas9-nls RNA (150 pg) were injected into Tg(-5.1mnx1:EGFP)/Tg(-5.1mnx1:TagRFP) double transgenic embryos. The control embryos were injected with nls-zCas9-nls RNA and a gRNA lacking the egfp target sequence. (A?I) Confocal images of spinal motoneurons of live zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf. In contrast to the uniform motoneuron EGFP expression pattern in the control (A), egfp-targeted embryos showed mosaic EGFP expression in the motoneurons (D and G). However, the motoneurons of the egfp-targeted embryos developed normally as indicated by the uniform TagRFP labeling (E and H). (J) BsrFI digestion showed high mutagenesis rates at the egfp target site (82?99%) in nine randomly selected egfp-targeted embryos. (K) Sequences of egfp mutations in 27 F1 embryos from two egfp-targeted Tg(-5.1mnx1:EGFP)-positive founders. The wild-type reference sequence is underlined with the target site and PAM highlighted in gray and red, respectively. Note that all 27 F1 siblings had egfp mutations with the BsrFI site (marked by a red line) disrupted. Deletions and insertions are indicated by dashes and lowercase red letters, respectively. The net change of each indel mutation is noted at the Right of each sequence (+, insertion; ?, deletion). The number of times a mutant allele was identified is indicated in brackets. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) |