Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131015-29
- Publication
- Zhang et al., 2013 - Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2: A novel gene involved in zebrafish central nervous system development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
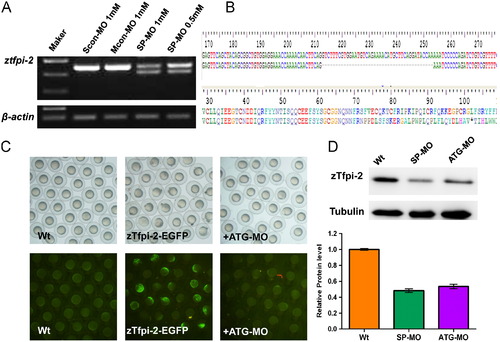
Efficiency of ztfpi-2 knockdown by MOs. (A) The SP-MO altered splicing in zebrafish. The results showed a MO concentration-dependent decrease of ztfpi-2 RNA levels, which indicated that the SP-MO successfully downregulated the expression of ztfpi-2 at 24 hpf. (B) Sequence comparison of ztfpi-2 revealed that 41 bp of exon 2 was lost due to a frameshift mutation after bp 71, leading to a stop codon at bp 102. (C) ATG-MO knockdown of the zTfpi-2-EGFP fusion protein at 8 hpf. Green fluorescence was detectable in a mosaic pattern throughout embryos injected with the zTfpi-2-EGFP plasmid at 38 pg, while GFP expression was absent in nearly all embryos co-injected with 0.6 mM ATG-MO and wild-type embryos without injection. (D) Western blot analysis of zTfpi-2 knockdown efficiency. Embryos injected with 0.5 mM SP-MO or 0.6 mM ATG-MO were harvested at 24 hpf. Tubulin was used as the loading control. Gray scale analysis showed that zTfpi-2 was reduced to 48% of former levels by SP-MO and to 53% by ATG-MO. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 381(1), Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Zhou, W., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Deng, S., Li, W., Li, H., Mao, Z., and Ma, D., Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2: A novel gene involved in zebrafish central nervous system development, 38-49, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.