Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130821-7
- Publication
- Anderson et al., 2013 - Hepatocyte Growth Factor Signaling in Intrapancreatic Ductal Cells Drives Pancreatic Morphogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
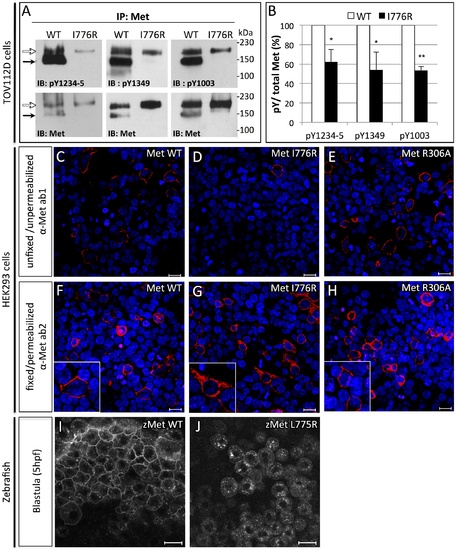
Orthologous murine donut mutation, I776R, impairs HGF signaling and receptor trafficking. (A) Immunoblots of Met protein prepared from lysates of TOV112D cells transfected with murine MetWT or MetI776R. Upper panels blotted with anti-pY show diminished phosphorylation at tyrosines critical for signaling and lower panels blotted with anti-Met show loading controls. Precursor (white arrows) and mature (black arrows) forms of MetWT are both detected, but MetI776R is only present in the precursor form. (B) Quantification by densitometry of phosphorylated Met versus total Met in panel A (t test, * p<0,05; **p<0,01). (C?H) Immunofluorescence staining of HEK293 cells transfected with MetWT (C,F), MetI776R (D,G), or furin cleavage-incompetent MetR306A (E,H). Unfixed, unpermeabilized cells were stained with anti-Met ab1, which binds an extracellular epitope (C?E), and fixed, permeabilized cells were stained with ab2, which binds an intracellular epitope (F?H). MetWT and MetR306A are localized to the plasma membrane (C, E, insets in F, H), but MetI776R is not (D), and is mostly retained in the cytoplasm (G, inset). Intracellular staining of Met demonstrates similar transfection efficiency. DAPI staining (blue) marks nuclei. (I?J) Live imaging of zebrafish blastulae injected with zebrafish MetWT-mCherry (I) and MetL775R-mCherry (J) at 5 hpf. Zebrafish MetL775R-mCherry largely fails to localize to the plasma membrane as compared to MetWT. Scale bars, 20 μm. |