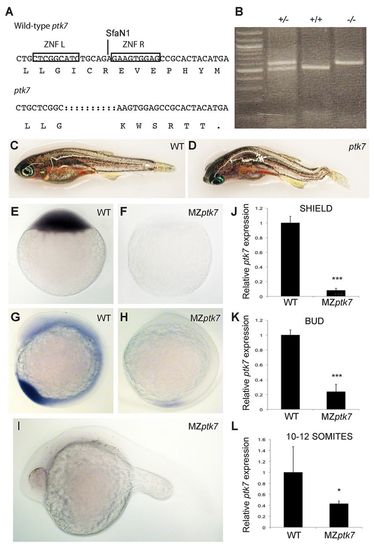
Ptk7hsc9 mutant transcript is targeted for non-sense-mediated decay (NMD). (A) Ptk7 ZFN target sequence and ptk7hsc9 mutant allele. Both the nucleotide and protein sequence are represented. Ptk7 ZFNs induced a 10-bp deletion, represented by dashed lines in the mutant sequence. This frame-shift mutation yields a premature termination codon immediately adjacent to the target site. Boxes outline the nucleotide target of left (ZFN L) and right (ZFN R) zinc-finger proteins. SfaN1 indicates the restriction site used to identify potential mutations. (B) Mutations were identified by PCR amplification of genomic DNA followed by SfaN1 restriction digest. Examples of wild-type (+/+), heterozygote (+/-) and mutant (-/-) zebrafish are represented. The Ptk7hsc9 allele is not targeted by SfaN1, and runs higher on a DNA gel than wild-type ptk7. (C,D) Wild-type (C) and zygotic ptk7hsc9 mutant (D) zebrafish at 2 months post-fertilisation. Axial curvatures were observed in 100% of ptk7hsc9 mutant juvenile and adult zebrafish. (E-I) ptk7 expression in wild-type (E,G) and maternal-zygotic ptk7hsc9 (MZptk7hsc9) mutant (F,H,I) embryos, as visualised by WISH at the one-cell (E,F), 10- to 12-somite (G,H) and 24 hpf (I) stages. (J-L) Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) reveals a strong reduction in ptk7 transcript in MZptk7hsc9 relative to wild-type at shield (J; ***P<0.001), bud (K; ***P<0.001) and 10- to 12-somite (L; *P=0.0358) stages. Error bars represent the s.e. for the expression level fold change.
|

