Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130424-15
- Publication
- Pistocchi et al., 2013 - Conserved and divergent functions of Nfix in skeletal muscle development during vertebrate evolution
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
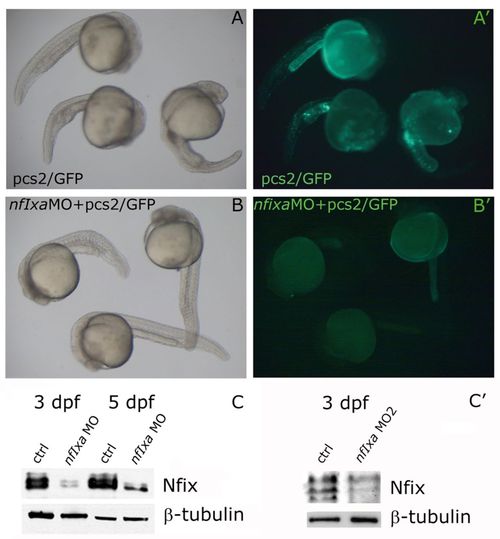
nfixa-MO specifically reduces nfixa-GFP sensor mRNA translation and Nfi protein levels. For the in vivo test of the specificity of nfixa-MO, an nfixa-GFP sensor has been generated. The pCS2+ construct containing the sequence recognized by the nfixa-MO fused with the GFP open reading frame was used for injection experiments with ctrl-MO or with the nfixa-MO. (A,A′) Embryos at 24 hpf: GFP-positive cells in the trunk and in the yolk epithelium following co-injection of the sensor and the control-MO. (B,B′) The complete absence of GFP expression when the sensor is co-injected with nfixa-MO confirms the specificity of the morpholino action. In A,A′, embryos are visualized under normal light; in B,B2 embryos are under fluorescent light. (C,C ) The morpholino efficiency has also been tested by means of western blot experiments; Nfix protein levels are decreased both in AUG-nfixa-MO (C) and splice-nfixa-MO2 (C′) injected embryos in comparison with control embryos at the same developmental stages. |