Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130110-24
- Publication
- Dalcq et al., 2012 - RUNX3, EGR1 and SOX9B Form a Regulatory Cascade Required to Modulate BMP-Signaling during Cranial Cartilage Development in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
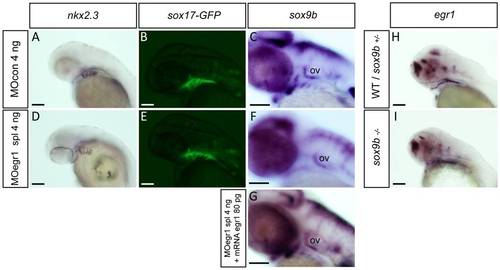
Egr1 is required for expression of sox9b in pharyngeal endoderm. Endodermal gene expression by in situ hybridization (A,C,D,F,G,H,I) or in living transgenic embryos (B,E) in control embryos (A?C,H), egr1 morphants (D-F), rescued embryos (G) and sox9b mutants (I) at 48 hpf. Lateral views, anterior to the left. Scale bars 100 μm. (A,D) nkx2.3 expression is not altered in 4 ng MOegr1 spl injected embryos. (B,E) In living sox17:GFP transgenic embryos, the transgene is correctly expressed in egr1 morphants. (D,F,G) The endodermal marker sox9b is not expressed in the pharyngeal endoderm in 4 ng MOegr1 spl injected embryos, but its expression is rescued upon co-injection of 80 pg egr1 mRNA and spl 4 ng MOegr1. (H, I) In homozygous sox9b-/- embryos, egr1 transcripts are still observed in the pharyngeal endoderm like in the wild-type or heterozygous sox9b+/- embryos. Pharyngeal endoderm (pe), otic vesicle (ov). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Protruding-mouth |