Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130102-2
- Publication
- Vemaraju et al., 2012 - A spatial and temporal gradient of fgf differentially regulates distinct stages of neural development in the zebrafish inner ear
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
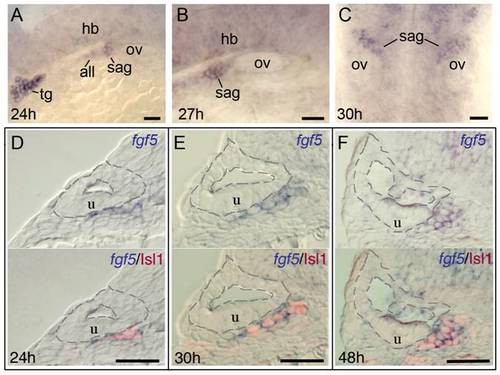
Mature SAG neurons express fgf5. (A-C) Wholemount embryos showing lateral views of fgf5 expression at 24 hpf (A) and 27 hpf (B) and a dorsal view at 30 hpf (C). During these stages, fgf5 expression marks the trigeminal ganglion (tg), anterior lateral line ganglion (all) and SAG, and there is also weak diffuse expression in the developing hindbrain (hb). There is no detectable staining in the otic vesicle (ov). (D-F) Transverse sections (dorsal to the top and lateral to the left) of specimens co-stained for fgf5 (blue) and Islet-1 (red) at 24 hpf (D), 30 hpf (E) and 48 hpf (F). Sections pass through the middle portion of the SAG at the level of the utricular macula (u). The inner and outer surfaces of the otic vesicle are outlined. Co-labeling confirms that fgf5 expression in the SAG is restricted to mature neurons. Scale bar, 25 μm. During mid-somitogenesis stages fgf5 is diffusely expressed throughout the neural tube and strongly marks the developing trigeminal ganglion (not shown). |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Antibody: | |
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Long-pec |