Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130102-19
- Publication
- Vij et al., 2012 - Evolutionarily Ancient Association of the FoxJ1 Transcription Factor with the Motile Ciliogenic Program
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
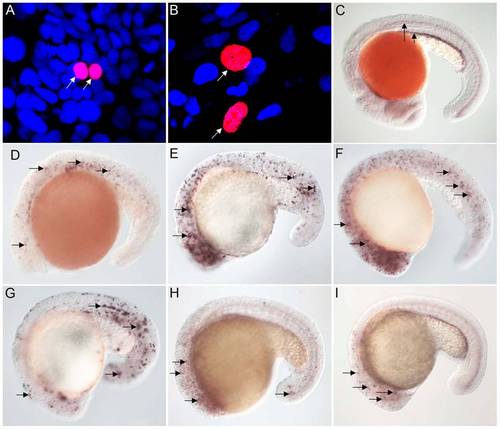
FoxJ1 from T. adhaerens and S. purpuratus are nuclear localized and can regulate the expression of ciliary genes. Anti-myc antibodies were used to detect Placozoa (A) and sea urchin (B) FoxJ1 (red, white arrow). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C) Expression of dynein intermediate chain in the spinal cord (long arrow) and pronephric (kidney) duct (short arrow) of a wild-type zebrafish embryo. The wdr78 and efhc1 genes are expressed in a similar pattern in wild-type embryos (see Figure 2A and data not shown). Ectopic expression of dynein intermediate chain in embryos ectopically expressing placozoan (D) and sea urchin (E) FoxJ1, respectively. Ectopic expression of wdr78 in embryos ectopically expressing placozoan (F) and sea urchin (G) FoxJ1, respectively. Ectopic expression of efhc1 in embryos ectopically expressing placozoan (H) and sea urchin (I) FoxJ1, respectively. Mis-expression of the different ciliary genes in D?I is indicated by the arrows. Embryos depicted are at 20 hpf, oriented anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 20-25 somites |