|
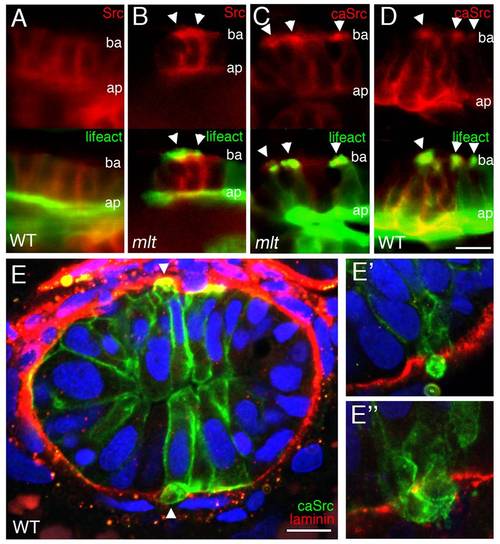
Src induces formation of invadopodia-like protrusions in the intestine of wild type zebrafish larvae. (A?D) Sagittal confocal scans through the intestine of 74 hpf wild type and mlt larvae that express Src-mCherry (red) and Lifeact-GFP (green) in the intestinal epithelium. (A) In WT, Src (red) is localized at the apical (ap) and lateral epithelial cell membrane. (B) In mlt, Src also localizes to sites of actin-rich (green) invadopodia-like protrusions (arrowheads B) arising from the basal epithelial cell membrane (ba). (C) Constitutively active Src (caSrc; red) localizes to invadopodia-like protrusions (green) in mlt (arrowheads). (D) caSrc induces formation of the protrusions in WT (arrowheads). (E) Histological cross-sections through the intestine of a 74 hpf wild type larva showing caSrc-rich protrusions (green) protruding through small degraded regions of the basal lamina (laminin immunostain, red). Additional examples are shown in high power images (E, E′, and E′′).
|