|
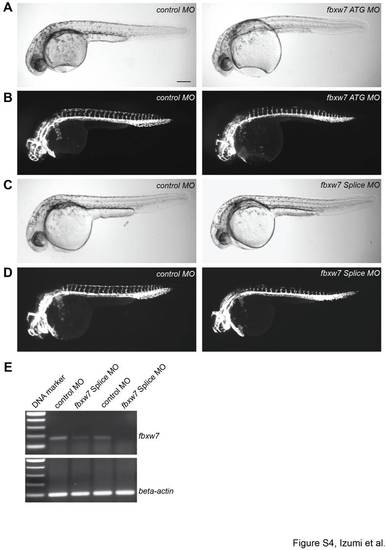
Vascular defects caused by the knockdown of zebrafish fbxw7. Bright-field images (A, C) and endothelial fluorescence (B, D) of Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 zebrafish embryos at 32 hpf injected with control (control MO), fbxw7 translation-blocking (ATG MO) or fbxw7 splicing-blocking (Splice MO) morpholinos, as indicated. The knockdown of fbxw7 impaired ISV outgrowth and prevented the formation of the DLAV, while the size and general growth of the morphant embryos were unaffected. Scale bar is 200 μm. PCR analysis (E) showing the reduction of fbxw7 transcripts in zebrafish embryos injected with Splice MO in two independent experiments. Beta-actin PCR products were used as loading control.
|