Fig. 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120612-8
- Publication
- Moro et al., 2012 - In vivo Wnt signaling tracing through a transgenic biosensor fish reveals novel activity domains
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
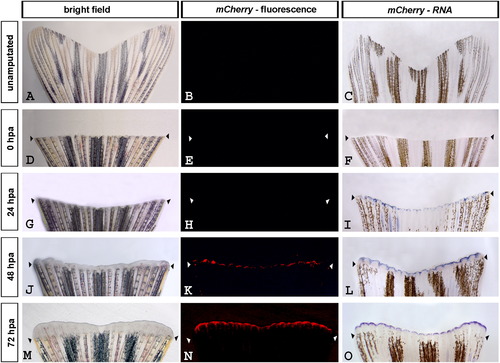
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is detectable in regenerating tail fins of Tg(7xTCF-Xla.Siam:nlsmCherry)ia5 fish. (Left column) Bright field live images of unamputated and regenerating fins. (Middle column) mCherry fluorescence in live unamputated and regenerating fins. (Right column) mCherry expression detected by RNA in situ hybridization in unamputated and regenerating fins. (A?C and D?F) Wnt/β-catenin signaling is not detectable in unamputated and newly amputated fish fins, respectively. (G?I) β-catenin activity is detected by strong mCherry RNA expression at 24 hpa while mCherry fluorescence is not visible yet. (J?L) mCherry expression is detectable by both RNA and fluorescence at 48 hpa. (M?O) Wnt/β-catenin signaling is robustly evident by both mCherry RNA and fluorescence at 72 hpa. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 366(2), Moro, E., Ízhan, G., Mongera, A., Beis, D., Wierzbicki, C., Young, R.M., Bournele, D., Domenichini, A., Valdivia, L.E., Lum, L., Chen, C., Amatruda, J.F., Tiso, N., Weidinger, G., and Argenton, F., In vivo Wnt signaling tracing through a transgenic biosensor fish reveals novel activity domains, 327-340, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.