Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120412-21
- Publication
- Veleri et al., 2012 - Knockdown of Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Gene BBS9/PTHB1 Leads to Cilia Defects
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
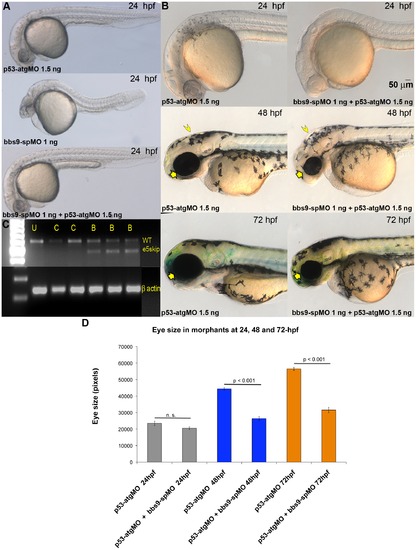
Exon 5-targeted bbs9 splice morpholino affects eye development independent of p53 pathway. (A) At 24 hpf, the p53-atgMO (1.5 ng) alone injection did not elicit a phenotype. The bbs9-spMO (1 ng) injection alone caused developmental defects in the eye, brain and tail of morphants. However, co-injection of p53-atgMO reduced the defects seen by the bbs9-spMO injection alone, though mild eye defect remained the tail becomes normal (bottom panel). (B) Higher magnification of morphants′ head region. Top, middle and bottom rows are 24-, 48- and 72-hpf, respectively. Left and right column of panels are p53-atgMO without and with bbs9-spMO, respectively. At 48 hpf the effect of bbs9-spMO injection on eye size visible (compare the arrows). The bbs9-spMO injection also resulted in hydrocephalous (compare the arrow heads). The defects seen at 48 hpf are weaker at 72 hpf. (C) The gel photograph of RT-PCR showing exon-skipping by bbs9-spMO. mRNA isolated from individual embryos was used for RT-PCR. U, C (4 and 6 ng) and B (1, 4, 6 ng) represent un-injected, control, and bbs9-spMO, respectively. Splice blocking gave an additional smaller (marked e5skip) band along with the original WT band. The bottom panel shows β-actin control for respective samples. (D) Quantification of the effect of morpholino(s) injection on eye size. X-axis shows the morpholinos used and time (hpf) of scoring. Y-axis shows eye size in pixels (mean ± SEM). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Protruding-mouth |