Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110720-17
- Publication
- Banerjee et al., 2011 - A novel role for MuSK and non-canonical Wnt signaling during segmental neural crest cell migration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
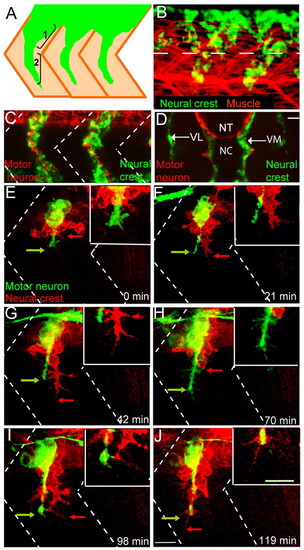
Wild-type neural crest and motor axon migration. (A) Schematic showing two stages of zebrafish neural crest cell migration: (1) initiation and (2) maintenance of segmental migration. Neural crest cells (green) migrate through a central region of the somites (tan). (B) Lateral view of a 22-hour-old embryo stained with a crestin riboprobe (green) marking neural crest cells and with F59 antibody marking adaxial muscle cells. Dashed lines mark the ventral boundary of the neural tube. (C) Lateral view of a 28-hour-old zebrafish embryo revealing neural crest cells in green (crestin riboprobe) and motor axons in red (znp-1/SV2 antibody cocktail). Dashed lines indicate approximate locations of somite boundaries. (D) Cross-sectional view of a 28 hpf embryo stained for neural crest cells (crestin) in green and motor axons (znp-1/SV2) in red. NT, neural tube; NC, notochord; VL, ventrolateral (or lateral) pathway; VM, ventromedial (or medial) pathway. Scale bar: 10 μm. (E-J) Still images from a time-lapse movie showing early co-migration of neural crest cells (red) and motor axons (green). Arrows point to filopodial extensions. Dashed lines indicate approximate locations of somite boundaries. Scale bar: 10 μm. See also Movie 1 in the supplementary material. |