Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110712-21
- Publication
- Bruses, 2011 - N-cadherin regulates primary motor axon growth and branching during zebrafish embryonic development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
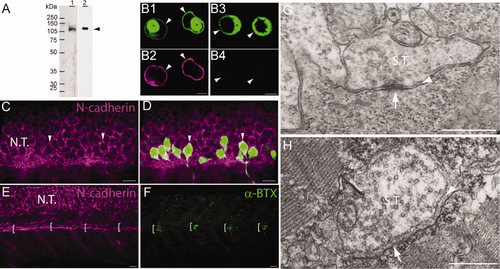
N-cadherin expression in primary motor neurons and muscle pioneer cells. A: Western blot analysis of anti-N-cadherin antibodies (see Table 1). Zebrafish (72 hpf) homogenates (40 μg of total protein/lane) were electrophoresed in a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, electrotransferred to a PVDF membrane, and immunoblotted with a rabbit polyclonal anti-zebrafish N-cadherin (lane 1) and MNCD2 monoclonal anti-mouse N-cadherin (lane 2) antibodies. A single band of <120 kDa was detected in lane 1 and lane 2 by the rabbit polyclonal and MNCD2 antibodies, respectively (arrowhead). B: CHO cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing Gal4 under a CMV promoter and a plasmid carrying zebrafish N-cadherin and pren-EGFP under a 14X-UAS element (B1,2) or a plasmid expressing pren-EGFP under a 14X-UAS (B3,4). Cells were fixed and immunostained with anti-N-cadherin MNCD2 antibodies and anti-rat IgG Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies. B1,2: Confocal images of the same cells showing expression of EGFP (B1) and N-cadherin (B2). B3,4: Confocal images of the same cells showing expression of EGFP (B3) while no N-cadherin labeling is detected (B4). Arrowheads point to the cell membrane, and asterisks indicate the perinuclear region. C,D: Neural tube of 24 hpf Tg(mnx1:GFP) embryos immunostained with anti-N-cadherin MNCD2 antibodies and observed under confocal microscopy. Arrowheads point to primary motor neuron cell bodies labeled with EGFP and expressing N-cadherin on the cell surface. E,F: Wild-type zebrafish embryos (24 hpf) doubly labeled with anti-N-cadherin MNCD2 antibodies (E) and with α-bungarotoxin (α-BTX) conjugated with Alexa 488 to detect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (F). Brackets indicate the muscle pioneer cells at the horizontal myoseptum expressing N-cadherin (E) and a distinct cluster of acetylcholine receptors (F). G: Electron micrograph of a neuromuscular junction at the horizontal myoseptum from a 24 hpf wild-type zebrafish embryo. The arrowhead points to the synaptic cleft and the arrow to an active zone. H: Electron micrograph of a neuromuscular junction from a 120 hpf wild-type zebrafish larva. The arrowhead points to the synaptic cleft containing a characteristic basal lamina and the arrow points to an active zone determined by the presence synaptic vesicles fused to the presynaptic membrane. NT, neural tube; ST, synaptic terminal. In C–F, rostral is to the left and dorsal is to the top. Scale bars = 5 μm in B; 10 μm in C–F; 0.5 μm in G,H. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.] |