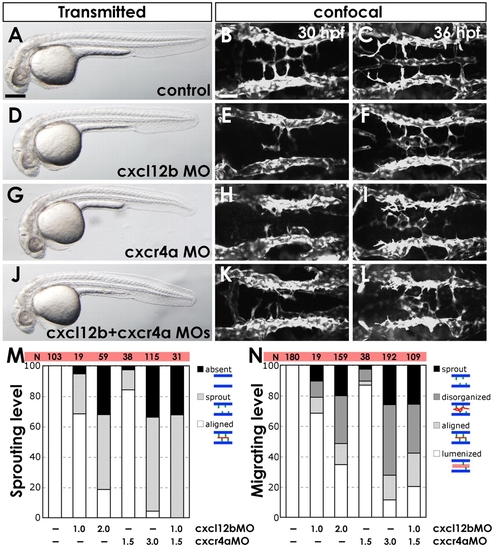
Chemokine signaling is required for hindbrain vascular patterning. (A-L) BA assembly defects are present in cxcr4a MO- and cxcl12b MO-injected Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 zebrafish embryos. (A,D,G,J) Transmitted light images of 32 hpf animals; lateral view, rostral to the left. (B,C,E,F,H,I,K,L) Confocal images of the hindbrain vasculature in 30 (B,E,H,K) or 36 (C,F,I,L) hpf animals; dorsal view, rostral to the left. Animals were injected with control MO (A-C), 2 ng cxcl12b-MO2 (D-F), 3 ng cxcr4a-MO2 (G-I), or 1 ng cxcl12b-MO2 + 1.5 ng cxcr4a-MO2 (J-L). (M) The percentage of 30 hpf MO-injected animals with no PHBC sprouts (?absent?), PHBC sprouts that do not extend to or align along the midline (?sprout?), or BA endothelial cells aligned along the ventral keel of the hindbrain (?aligned?, which is normal for this stage). (N) The percentage of 36 hpf MO-injected animals with PHBC sprouts that do not extend to or align along the midline (?sprout?), BA endothelial cells near the midline but not aligned longitudinally (?disorganized?), endothelial cells aligned along the ventral keel of the hindbrain but not lumenized (?aligned?), or with an assembled, lumenized BA (?lumenized?, which is normal for this stage). For illustration of phenotypic categories, see Fig. S7 in the supplementary material. Scale bars: 250 μm in A; 50 μm in B.
|

