Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110407-36
- Publication
- Kikuchi et al., 2011 - Retinoic Acid production by endocardium and epicardium is an injury response essential for zebrafish heart regeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
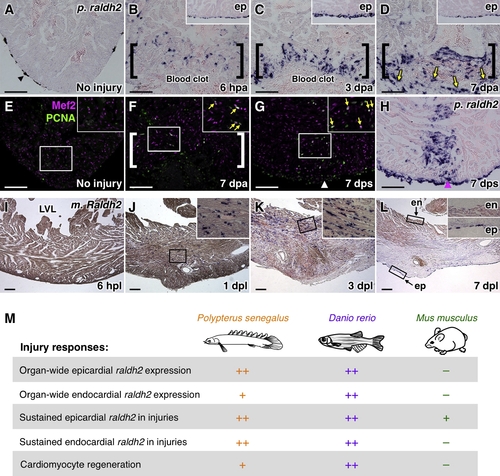
Cardiac Injury Responses in Polypterus, Mouse, and Zebrafish (A?D) raldh2 (p. raldh2) expression by in situ hybridization in uninjured (A) and injured (B?D) polypterus ventricles. Arrowheads in (A), pigment cells. Brackets in (B?D), injury site. Insets in (B?D), lateral ventricular wall including epicardium (ep). Arrows in (D), p. raldh2-expressing epicardial cells. Scale bar represents 100 μm (A?H). (E?G) Assessment of Mef2+PCNA+ cells (arrows) in uninjured (E) and injured (F and G) polypterus ventricles. Brackets in (F), injury site. Insets, high-zoom images of the rectangle. Arrowhead in (G), entry site of glass needle. Arrows in (F and G), proliferating CMs. (H) In situ hybridization of p. raldh2 after stab injury (arrowhead). (I?L) Raldh2 (m. Raldh2) expression by in situ hybridization at various time points post-ligation (pl). Insets in (J?L), high-zoom images of the rectangle. ep, epicardium; en, endocardium; LVL, left ventricular lumen. Scale bar represents 200 μm. (M) Summary of injury responses observed in polypterus, zebrafish, and mouse hear |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 20(3), Kikuchi, K., Holdway, J.E., Major, R.J., Blum, N., Dahn, R.D., Begemann, G., and Poss, K.D., Retinoic Acid production by endocardium and epicardium is an injury response essential for zebrafish heart regeneration, 397-404, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell