Fig. 2
|
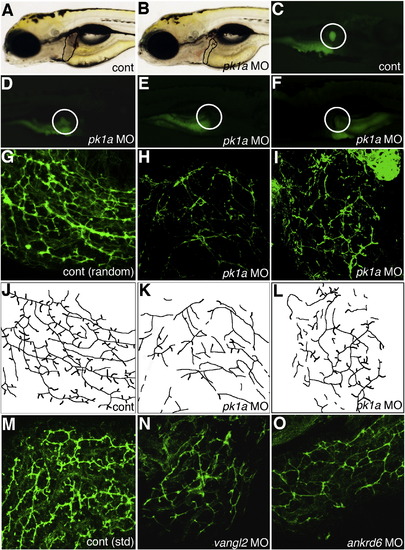
Altered PED6 gallbladder uptake and bile duct defects in pk1a morphants. (A?B) Left lateral view of live 5 dpf control (A, cont) and pk1a morpholino-injected (B, pk1a MO) larvae. Liver size (black outline) appears smaller in (B), but otherwise the larvae appear similar. (C?F) PED6 uptake in control (C) and three examples of pk1a morphants (D?F), showing decreased uptake (D), no uptake (E), and abnormal left-sided placement of the gallbladder (F) in pk1a morphants. Note that the view of (C?E) is right lateral and that of (F) is left lateral to show the gallbladder sidedness. (G?I) Confocal projections of whole-mount cytokeratin immunostainings of random control MO-injected (G) and pk1a morphant (H, I) livers at 5 dpf demonstrate decreased number and complexity of intrahepatic bile ducts in the pk1a morphants. (J?L) Line schematics of ducts in (G?I) to clarify the duct staining pattern. (M?O) Confocal projections of whole-mount cytokeratin immunostainings of livers from 5 dpf larvae injected with standard (std) control MO (M) and larvae injected with MOs against vangl2 (N) or ankrd6 (O). Note that the pattern of the ducts in (N) and (O) is similar to the ducts in the pk1a MO-injected larva (H, I). Similar results were obtained with either the AUG or splice blocking pk1a, vangl2, and ankrd6 MOs. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 351(2), Cui, S., Capecci, L.M., and Matthews, R.P., Disruption of planar cell polarity activity leads to developmental biliary defects, 229-241, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.