Fig. 3
|
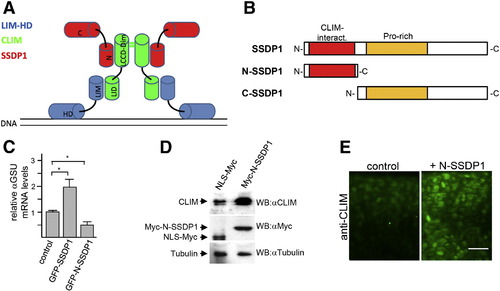
N-SSDP1 inhibits LIM-HD transcriptional complex in vitro and stabilizes CLIM in vivo. A: Model of transcriptional complexes consisting of LIM-HDs (blue), CLIM (green) and SSDP1 (red) on DNA. LIM domain (LIM); homeodomain (HD); LIM interaction domain (LID); Ldb/Chip conserved domain (LCCD); dimerization domain (dim); N- and C-terminal portions of SSDP1 (N and C, respectively) are indicated. B: N-SSDP1 contains the CLIM-interacting domain, but not the proline-rich domain. C-SSDP1 lacks the CLIM-interacting domain of SSDP1. C: Over-expression of full length SSDP1 in αT3 cells significantly increases transcriptional activity of LIM-HD factors in these cells whereas GFP-N-SSDP1 decreases it, as indicated by relative levels of the target αGSU mRNA measured by RT-qPCR. D: Western blot analysis of embryos (24 hpf) after over-expression of myc-tagged N-SSDP1 shows increased CLIM protein levels as compared to embryos injected with control mRNA for myc-tagged NLS. E: N-SSDP1 mRNA injection increases CLIM immunofluorescence in embryos, confirming Western Blot results. Lateral views of the trunk region of whole-mounted embryos (24 hpf) are shown. Scale bar = 25 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 349(2), Zhong, Z., Ma, H., Taniguchi-Ishigaki, N., Nagarajan, L., Becker, C.G., Bach, I., and Becker, T., SSDP cofactors regulate neural patterning and differentiation of specific axonal projections, 213-224, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.