Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110112-35
- Publication
- Mosimann et al., 2011 - Ubiquitous transgene expression and Cre-based recombination driven by the ubiquitin promoter in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
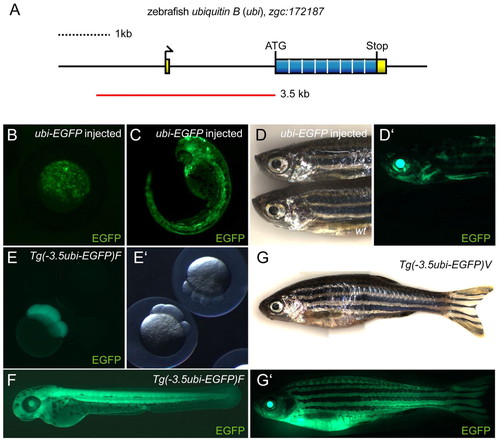
Cloning and characterization of the zebrafish ubi regulatory region. (A) Schematic of the zebrafish ubiquitin B locus zgc:172187 on linkage group 5, featuring a 71 bp non-coding first exon, a single 2 kb intron and a coding exon containing the ORF for a Ubiquitin octamer peptide. The red line indicates the PCR-amplified and subcloned 3.5kb ubi promoter fragment. (B-D′) EGFP fluorescence images of zebrafish injected with Tol2(–3.5ubi:EGFP) vector at the one-cell stage, (B) oblong to sphere stage (approx. 4 hpf), (C) 36 hpf, and (D,D′) adult. Note the transgene injection-derived mosaic EGFP expression that persists through all developmental stages compared with wild type. (E-G′) ubi:EGFP expression in stable transgenic lines. (E) Maternal EGFP contribution in embryos derived from outcrossing an F2 stable transgenic Tg(–3.5ubi:EGFP)F female to wild type compared with a transgene-negative sibling, here shown at the eight-cell stage (1.25 hpf). (F) ubi-EGFP expression at 48 hpf in offspring resulting from outcrossing of a F2 Tg(–3.5ubi:EGFP)F male to wt. (G,G′) Compound image overview of an adult zebrafish female heterozygous for Tg(–3.5ubi:EGFP)V, revealing widespread EGFP fluorescence including in the fins. wt, wild type. |