|
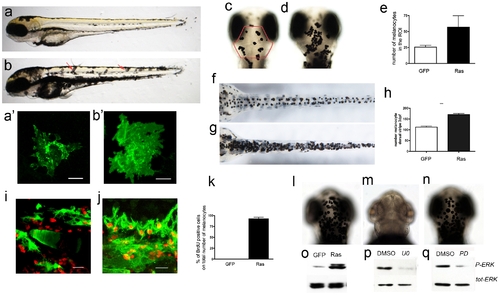
Expression of oncogenic HRAS driven by kita promoter induces hyperpigmentation in larvae. a) A 3dpf wild-type zebrafish; b) a kita-GFP-RAS hyperpigmented transgenic with displaced melanocytes (red arrows). A′-b′) size and shape of representative head melanocytes in control (a′) and kita-GFP-RAS embryos (b′) c?e) Dorsal views of the head of control (c) and kita-GPF-RAS larvae (d). The red outline in (c) indicates the ROI where counts were made. e) Quantification of the number of melanocytes (mean±SD) (mean±SD, ***p<0.001) as indicated. f?h) Dorsal views of the lower body of control (f) and kita-GPF-RAS larvae (g). h) Quantification of the number of melanocytes (mean±SD, ***p<0.001) as indicated. i?k) GFP marked melanocytes (green) and BrdU immunostaining (red) in kita-GFP (i) and kita-GFP-RAS (j) 4dpf zebrafish. Calibration bar: 20 μm. k) Percentage of BrdU+ melanocytes in control (GFP) and melanoma line (Ras) at 4dpf (mean±SD, n = 5). l?n) Dorsal views of heads of kita-GFP-Ras larvae raised in DMSO (l), in U0126 (m) or in PD98059 (n) in the presence of epinephrine. o) WB analysis performed 3dpf GFP (control larvae) and RAS (kita-GFP-RAS larvae) revealed an activation of P-ERK. p?q) Treatment with UO126 (UO) or PD98059 (PD) caused a reduction of P-ERK. Calibration bars: 50 μm for a, b, c?f, l?n; 20 μm for i?j.
|