Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101123-67
- Publication
- Chung et al., 2010 - Suppression of Alk8-mediated Bmp signaling cell-autonomously induces pancreatic ?-cells in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
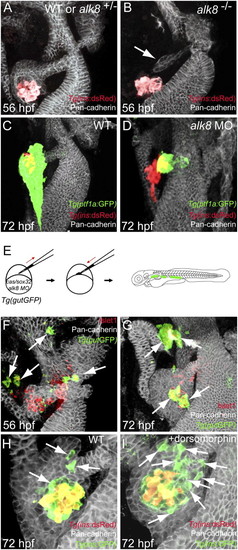
Suppression of Bmp signaling in a cell-autonomous fashion leads to an increase in ventral bud-derived endocrine cells. (A and B) Confocal projection of control (A) and alk8 mutant (B) endoderm at 56 hpf. Tg(ins:dsRed) embryos were stained for Pan-cadherin (white). (B) alk8 mutants exhibit a very small ventral pancreatic bud (arrow). (C and D) Confocal projections of control (C) and alk8 morphant (D) Tg(ptf1a:GFP);Tg(ins:dsRed) embryos stained for Pan-cadherin (white). In alk8 morphants (D), the ventral pancreas buds out but fails to expand and engulf the principal islet. (E) Schematic diagram of the cell transplantation protocol. Tg(gutGFP) donors were injected with cas/sox32 mRNA and alk8 splice-blocking MO, and the donor cells were transplanted into wild-type hosts. (F and G) Confocal projections of hosts containing alk8 morphant donor cells (green) stained for Pan-cadherin (white) and Islet1 (red) at 56 (F) and 72 (G) hpf. Most alk8 morphant donor cells gave rise to Islet1-expressing endocrine cells (arrows). (H and I) Confocal projections of Tg(ins:GFP);Tg(ins:dsRed) embryos stained for Pan-cadherin (white) comparing control (H) and dorsomorphin-treated (I) embryos. Compared with control embryos (H), dorsomorphin-treated embryos showed an increased number of GFP-only-positive β-cells (arrows) (I). |