Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101123-28
- Publication
- Knopf et al., 2010 - Dually inducible TetON systems for tissue-specific conditional gene expression in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
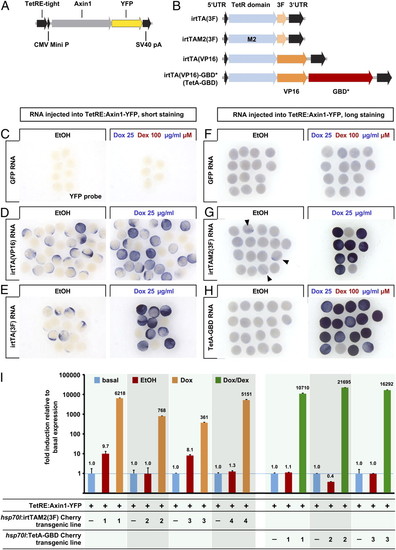
Dually inducible TetA-GBD activates transgene transcription in a nonleaky fashion in zebrafish embryos. (A) Transgenic Tet responder construct. (B) Human codon optimized (?improved?) variants of the reverse tetracycline-responsive transactivator (irtTA) used in this study. (C?H) YFP RNA expression detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization in TetRE:Axin1-YFP transgenic embryos injected with equimolar amounts of GFP (25 pg), irtTA(VP16) (30 pg), irtTA(3F) (25 pg), irtTAM2(3F) (30 pg), or irtTA(VP16)-GBD* (TetA-GBD, 50 pg) and treated with EtOH vehicle or 25 μg/mL Dox or 25 μg/mL Dox plus 100 μM Dex from 5 hpf for 4.5h (C?E) or 3.5h (F?H). Samples in F?H were stained significantly longer than those in C?E to reveal even low levels of leakiness. Note severe leaky induction in irtTA(VP16) and irtTA(3F) injected embryos and weak leakiness in irtM2(3F) injected embryos (arrowheads). (I) Axin1-YFP RNA expression detected by QPCR in progeny of TetRE:Axin1-YFP fish crossed with individual sublines of hsp70l:irtTAM2(3F)-p2a-mCherry or hsp70l:TetA-GBD-p2a-mCherry transgenic fish, heatshocked at 24 hpf, and treated with EtOH or 25 μg/mL Dox or Dox plus 100 μM Dex for 4 h. Levels are normalized to expression in TetRE:Axin1-YFP embryos containing no TetActivator transgene (?basal?). |