FIGURE
Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101021-59
- Publication
- Fukazawa et al., 2010 - poky/chuk/ikk1 is required for differentiation of the zebrafish embryonic epidermis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 4
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
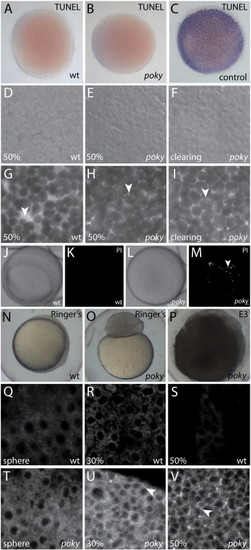
| Stage Range: | Sphere to 50%-epiboly |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 346(2), Fukazawa, C., Santiago, C., Park, K.M., Deery, W.J., Canny, S.G., Holterhoff, C.K., and Wagner, D.S., poky/chuk/ikk1 is required for differentiation of the zebrafish embryonic epidermis, 272-283, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.