Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101011-10
- Publication
- Garavito-Aguilar et al., 2010 - Hand2 ensures an appropriate environment for cardiac fusion by limiting Fibronectin function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
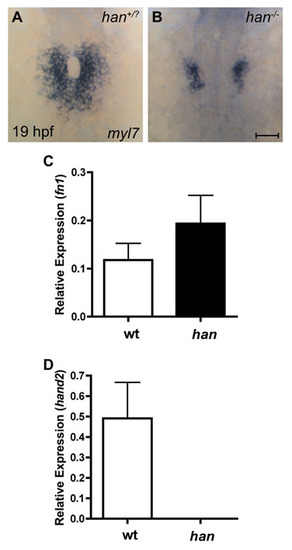
Heightened levels of fn1 expression in han mutants. (A,B) In situ hybridization for myl7 illustrates the han mutant phenotype at the stage when embryos were collected for RNA extraction and microarray analysis. Dorsal views, anterior up. Scale bar: 50 μm. (A) Wild-type cardiomyocytes have initiated cardiac fusion with contacts between posterior subsets of contralateral cells and are proceeding to complete formation of the cardiac cone with the merger of anterior subsets of contralateral cells. (B) By contrast, han mutant embryos exhibit two separated populations of cardiomyocytes. (C,D) Bar charts indicating levels of gene expression, relative gapdh, as detected by qRT-PCR in wild-type and han mutant embryos. Values represent the mean (ąs.e.m.) from triplicate samples. (C) Microarray analysis revealed a 2.0-fold upregulation of fn1 in han mutants (see Table S1), and validation of this result by qRT-PCR indicated that fn1 expression is increased 1.6-fold in han mutants. (D) Expression of hand2 was undetectable by qRT-PCR in han mutants, whereas microarray analysis indicated a 5.3-fold downregulation of hand2 in han mutants (see Table S1). PCR primers used were: fn1, 52-GAATCCCCGAGCCAATCAA-32 and 52-TTTTATGTTTCCCCGTTCCTT-32 hand2, 52-TGCGCTCGAATCAACAAATG-32 and 52-TATACCCTACGGCGAACCACA-32 gapdh, 52-CCCCACCCCCAATGTCTCT-32 and 52-AACCTGGTGCTCCGTGTATCC-32. |