Fig. 4
|
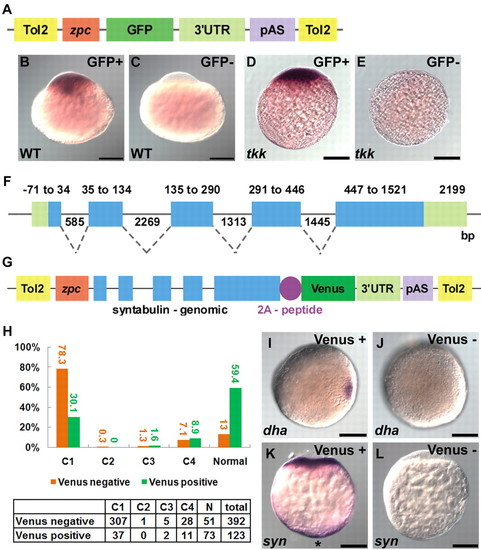
Exon-intron structure of syntabulin is required for vegetal localization and proper dorsal determination. (A-E) The 3′ UTR is not sufficient for vegetal localization of syntabulin. (A) Structure of the transgene plasmid. (B-E) Localization of GFP mRNA in transgenic (B,D) or non-transgenic (C,E) tkk (D,E) or wild-type (B,C) zebrafish embryos at the 1-cell stage (20 mpf). (F,G) Genomic structure of syntabulin (F) and the rescue plasmid that contains the exon-intron structure of syntabulin. 2A-peptide, 2A peptide of PTV1. (H) Rescue by genomic DNA. The numbers (tabulated) and percentages (bar chart) of transgenic (green) and non-transgenic (orange) embryos showing each phenotype. (I,J) Expression of dha in tkk (J; 9%, n=32) and rescued (I; 66%, n=33) embryos at the late blastula stage. (K,L) Localization of syntabulin at the 1-cell stage in a rescued (K; 86%, n=35) versus control (L; 100%, n=31) embryo. Shown are animal pole views (I,J) and lateral views (A-E,K,L). Vegetal pole localization is marked by an asterisk (K). Scale bars: 200 μm. |