Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090915-40
- Publication
- Chen et al., 2009 - Repression of RNA polymerase II elongation in vivo is critically dependent on the C-terminus of Spt5
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
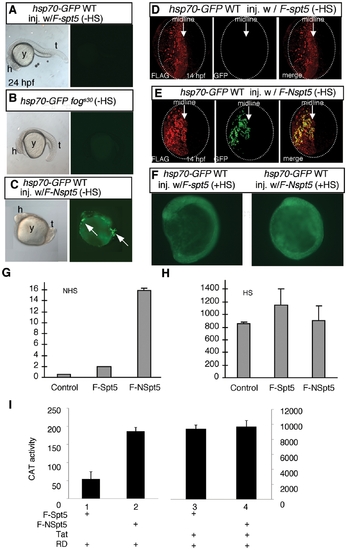
NSpt5 de-represses hsp70-4 expression in the absence of heat shock. (A?C) Embryonic morphology or GFP fluorescence of hsp70-GFP transgenic embryos. hsp70-GFP transgenic WT injected with F-spt5 RNA (A), hsp70-GFP transgenic fogs30 mutant (B), and hsp70-GFP transgenic WT injected with F-Nspt5 RNA (C). (D?E) Confocal images of FLAG- and GFP- double immuno-labeled embryos, injected with F-spt5 RNA (D), or with F-Nspt5 RNA (E). (F) GFP fluorescence in hsp70-GFP transgenic embryos injected with F-spt5 RNA (left) or F-Nspt5 RNA (right) and subjected to heat shock for one hour. (G?H) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis shows de-repression of hsp70-4 expression in 6 hpf Nspt5-expressing embryos (G), and no significant difference of hsp70-4 expression between F-Nspt5-expressing, F-Spt5-expressing, and control embryos upon heat shock (H). (I) F-NSpt5 increases transcription from the HIVLTR. CAT activity of Hela cells that express RD and F-Spt5 (lanes 1 and 3), or F-NSpt5 (lanes 2 and 4), in the absence (lanes 1 and 2) or presence of Tat (lanes 3 and 4). Results are presented in arbitrary units. Error bars represent S.E.M. from three independent experiments. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |