Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090904-10
- Publication
- Olesnicky Killian et al., 2009 - A role for chemokine signaling in neural crest cell migration and craniofacial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
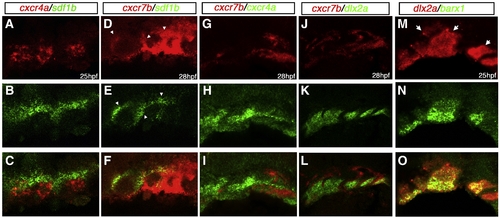
Double in situ hybridization of cxcr4a/cxcr7b/sdf1b in the developing pharyngeal arches. Lateral views, anterior to the left. Confocal micrographs of double fluorescent in situ hybridization of cxcr4a, cxcr7, sdf1b, dlx2a and barx1 in the pharyngeal arch region. (A?C) cxcr4a (red) is largely excluded from sdf1b (green) in the arches, but is slightly coexpressed with sdf1b at the endodermal border. (D?F) cxcr7b (red) is coexpressed with sdf1b (green) throughout the medial endoderm and anterior pharyngeal pouches at 28 hpf (arrowheads). (G?I) cxcr4a (green) is mostly excluded from cxcr7b (red) expressing cells, but does show some coexpression in the posterior pharyngeal region. (J?L) cxcr7b (red) is excluded from the dlx2a expressing CNCCs in the anterior arches but does show partial overlap with dlx2a expressing cells of the posterior pharyngeal arches. (M?O) barx1 is coexpressed with dlx2a in the ventral and medial portion of the pharyngeal arches but is reduced or absent in the dorsal arch (arrows). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 333(1), Olesnicky Killian, E.C., Birkholz, D.A., and Artinger, K.B., A role for chemokine signaling in neural crest cell migration and craniofacial development, 161-172, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.